This technology is designed to provide secure payments while purchasing services or products online. The first protocol was an idea suggested by VISA payment system, which was VDV – Verified by Visa. Later on, MasterCard created its protocol – MasterCard SecureCode (MCC) that would work the same way.
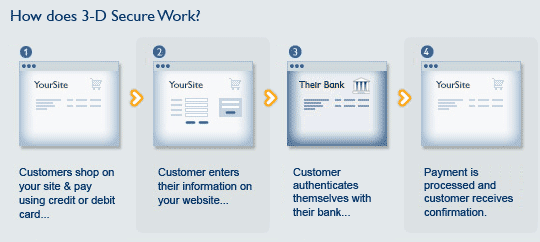
- 1Customer places the desired products in the shopping cart;
- 2Customer fills in the credit card number, expiration date, card holder's name and the card verification code (CVC2);
- 3Within the 3D Secure protocol, the website of the store redirects the customer to the card issuing bank. Where additional verification code is to be entered. There are several ways for the customer to receive the verification code: via SMS, from a single-use code cards or through a special device. The code can also be set by the customer and never change. All the information input by the customer is stored the payment server of the card issuing bank and the online store has no access to it. This protects the data from being thieved;
- 4After the transaction is completed on the card issuing bank's page, the customer is redirected to the page where all the transaction information is shown.
The online stores that use 3D Secure protocol can be easily recognized by the following logos placed on their web pages:

Authorization is a request to execute an operation using a bank card, resulting either permission or denial from the card issuing bank. The authorized amount becomes blocked on the customer's card while waiting for further actions: Withdrawal(Settle) or Return(Void).
If non of the operations (Settle or Void) have followed within a 30 day period, the amount unblocks automatically.
It is the operation that implies a withdrawal confirmation of earlier authorized funds from the customer's account in favor of the merchant.
It is the operation that implies a block cancellation of the earlier authorized funds on the customer's card.
Refund is the return of funds that have been earlier withdrawn from the customer's account as a payment for provided services or purchased merchandise. The refund is executed per customer's request and can be issued partially (less shipping fee, for example).
After the refund is completed, the funds are usually returned to the customer's account within a week.
In case the merchant is refusing to issue a refund, the customer's can still return the funds through a Chargeback, i.e. cancel the charge with the bank.
Chargeback is the process where the card issuing bank cancels the card operation, made by the the customer in an online store.
The procedure is initiated by the card holder. He submits the respective request to the bank where explains the reason why he considers the operation to be invalid or fraudulent.
The credit card company, in its turn, executes its own investigation and in case the customer is right, withdraws from the merchant's account the disputed amount and returns it to the customer's account, thus the chargeback made at the expenses of the merchant, who also pays the chargeback fee in order to cover the funds return procedure.
Chargeback can be initiated due to one of the following reasons:
- The merchant refused to issue a refund;
- There was a double charge on the customer's card;
- The withdrawn amount differs from the total amount of the purchase;
- The date and time of the operation are invalid;
- The signatures on the invoice differs from the one on the card statement;
- The customer's card was charges for a purchase we did not make;
- The money was withdrawn from the card but the customer has not received the merchandise or service;
- The customer is not satisfied with the merchandise or service: the actual product differs from what was shown or promised by the merchant or the services were not fully provided;
- The merchant refused to receive the product back.







